Recently updated on October 7, 2025
The internet has come a long way since its inception. Now it’s a powerful and influential tool that is an integral part of our lives. Yet, it’s not without flaws. Many recognize its pressing problems: lack of privacy, security, and centralized power.
Web3, the idea of a new version of the internet, aims to resolve those issues by bringing power back to users and revolutionizing the internet as we know it.
Being in its infancy, Web3 has great disruptive potential. That’s why it’s essential to understand this concept and be aware of a possible revolution on the Web.
In this article, we’ll discuss the following:
- Understanding Web3: A Guide to the Next Evolution of the Web
- Core Technologies and Elements of Web3
- Key Concepts Driving the Web3 Ecosystem
- Why Web3 Is Important
- Web3: use cases
- Looking ahead
Understanding Web3: A Guide to the Next Evolution of the Web
Web3 is often perceived as a fuzzy and evolving concept because it represents the next major shift in how the internet is built and experienced. While public awareness is still limited, it is steadily growing despite market challenges such as the crypto winter.
At its core, Web3 is a new iteration of the internet designed to be fair, transparent, and decentralized. Unlike today’s Web2, dominated by big tech companies that control content and monetize user data, Web3 applications (known as dApps) run on blockchain technology, ensuring data ownership and control remain with the users themselves.
In this new paradigm, user activities and data are stored across distributed networks rather than centralized servers. This shift empowers individuals by offering:
- Permissionless access – no gatekeepers controlling entry to the network.
- Censorship resistance – no single entity can block or remove content.
- True data ownership – users decide whether to keep their data private or monetize it.
Ultimately, Web3 combines blockchain, smart contracts, and digital assets (cryptocurrencies and NFTs) to reshape both user experiences and business models in the digital landscape.
What does Web3 mean for the users?
Put briefly, it will give users power once stolen by centralization.
Web3 will ensure permissionless (no gatekeepers control the network), censorship-free (no one can block you), and trustworthy(no middleman) access to the network and return the users’ full control over their own data. Users become the sole owners of their data and may choose to sell it to earn tokens or keep it private(encrypted) if they want to.
Why is Web3 important?
It’s important for two main reasons:
- Not only will Web3 change how users experience the internet, but it will also uplift their status in the network. Now, big tech companies won’t have access to user data so easily and can’t trade it to marketers.
- Such a shift in user status will inevitably bring major changes in business models and force businesses to adapt and seek new ways of approaching consumers in the new digital landscape.
Evolution of the Web
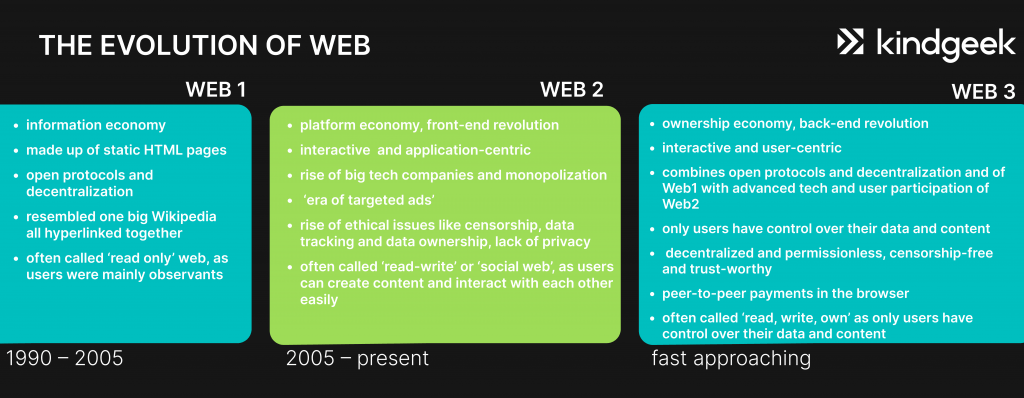
Every good explanation of Web3 meaning points out what previous versions of the internet looked like.
If you’re already familiar with this, you may skip it; if not, here’s the gist.
Web3 is a blend of the previous two eras of the internet – Web1 and Web2.
Open protocols and decentralization(Web1) + advanced tech and massive user interaction (Web2) = Web3
| Era | Description | Key Features |
| Web1: The Static Web (1990–2005) | The first version of the internet, mainly informational and “read-only.” | Static HTML pages, decentralized infrastructure, limited user interaction. |
| Web2: The Interactive & Centralized Web (2005–present) | The current internet era, highly interactive and application-centric but controlled by major platforms. | Social media, targeted ads, data centralization, ethical issues like privacy and censorship. |
| Web3: The Decentralized Web (emerging) | The next phase, combining decentralization of Web1 with the interactivity of Web2. | “Read, write, own” model, blockchain-based, user-centric, permissionless, censorship-resistant. |
Core Principles of Web3
To fully grasp how Web3 works, it’s crucial to understand the core principles shaping this next evolution of the internet. These ideas explain the shift from centralized platforms toward a user-owned, decentralized model built on blockchain and Web3 technologies.
Decentralization
Web3 distributes control and data storage across networks of independent nodes rather than relying on centralized servers. This eliminates single points of failure, prevents monopolistic control, and makes censorship far more difficult to impose.
Blockchain Technology
The foundation of how does Web3 work lies in blockchain — a secure, transparent ledger that enables decentralized applications (dApps). It ensures data integrity and trust without intermediaries, powering peer-to-peer interactions and digital asset management.
Token-Based Economy
Web3 introduces tokens — from cryptocurrencies to NFTs — that reward contributions, enable transactions, and create entirely new digital economies. This model encourages participation and aligns the incentives of users and developers.
User Sovereignty & Privacy
A defining feature of blockchain and Web3 is that users reclaim full ownership of their data and identities. They can choose to keep information private, monetize it, or transfer it across platforms without reliance on centralized entities.
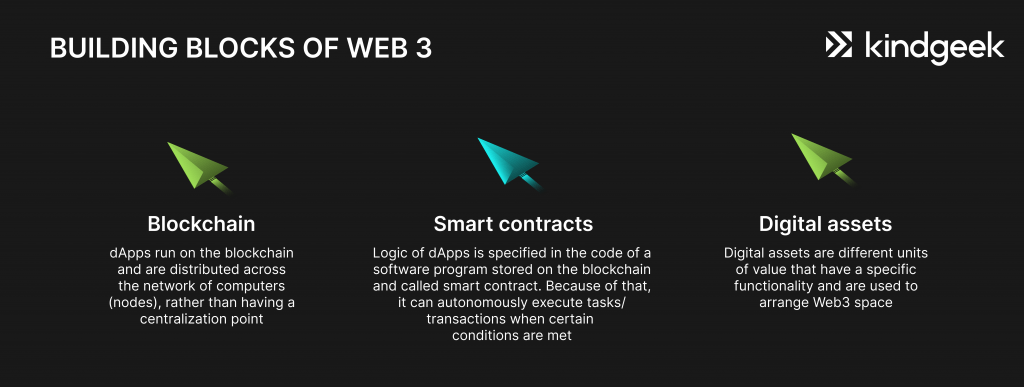
Core Technologies and Elements of Web3
Web3 is made up of three 3 tech fundamentals, and those are blockchain, smart contracts, and digital assets. Let’s briefly explore each of these Web3 concepts.
Blockchain
Put simply, blockchain is a big shared database. Any participant can read and add data to it, but nobody can change or delete anything there. That’s all because any shift affects the following blocks, and any change can be easily traced within multiple copies of the database. Thus, blockchain is often called ‘immutable’ or resistant to change.
Blockchain is used for recording and storing information on the internet. Currently, it’s mostly data on asset ownership (e.g., cash, land, intellectual property, etc.) and the history of transactions.
How does Blockchain Work
Instead of a centralized entity, regular users of the network carefully validate blockchain transactions to earn rewards (tokens) and reach an agreement (consensus), and authenticate transactions. Once validated, transactional data is added to the blockchain, and the new ‘block’ (data segment) is created and permanently linked or ‘chained’ to the previous blocks.
This original block is then duplicated across the network, and all nodes receive an encrypted copy of the block. Each time a new block is added, all nodes update to reflect the change.
What Makes Blockchain Exceptional
- decentralized and encrypted;
- ensures transparency among all stakeholders;
- can’t be hacked or manipulated.
Smart contracts
A smart contract is software stored on a blockchain. It represents application logic and can perform tasks autonomously based on a predefined set of rules written in the code of the ‘contract’.
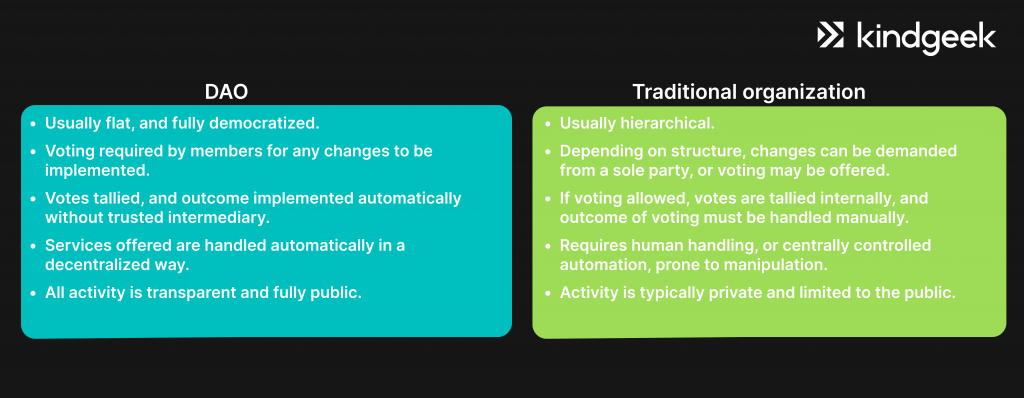
No one owns the code of the smart contract; it’s transparent for all stakeholders and can be changed if the users find it necessary. It will happen through a form of collective governance called a decentralized autonomous organization or DAO.
DAOs are blockchain-based organizations that operate towards shared goals: all users vote on changes and modifications, and define dApps future direction in such a way.
How do Smart Contracts Work?
When someone attempts to, let’s say, make a payment, the smart contract checks whether conditions meet predefined criteria and executes the transaction if everything is alright.
Smart contracts facilitate direct interaction between stakeholders without any central authority, in our case, without a bank.
Digital assets and tokens
Digital assets and tokens are the final element of Web3. They are verifiable and ownable digital items that represent units of value in the Web3 ecosystem. These assets are an indivisible part of the digital user experience as they exist on the blockchain across the dApps and can engage with smart contracts.
Information on asset ownership is no longer stored in centralized databases but on blockchain as a decentralized database. This means they can be put to use, for example, traded, anytime without a third party being involved.
In general, there are five types of digital assets as of now:
- Native tokens – digital monetary assets of a specific blockchain used to reward nodes for maintaining and updating the data on that blockchain.
- Stablecoins – fixed-price cryptocurrencies that represent cash on the blockchain. Their value is backed by the market value of fiat currencies like the US dollar or central bank digital currencies (CBDCs), regulated by a central bank.
- Governance tokens – a type of cryptocurrency that gives its holders the right to vote on proposed changes and shape the future of the platform.
- Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) – are “one-of-a-kind” digital items that contain a unique digital signature that proves the user’s sole ownership; almost everything can be converted into an NFT, even a tweet.
- Digital assets – represent ownership of a real-world asset such as land, commodities, or intellectual property that is “tokenized” into divisible digital assets on the blockchain.
If you are looking for a trusted partner, experienced in blockchain, smart contracts, digital assets, or any other crypto solutions development, consider Kindgeek. From ideation to deployment and beyond, our team guides you through the entire process of developing innovative cryptocurrency and blockchain-powered fintech products, with a focus on transparency, user experience, and bulletproof security.
Now that you have a brief understanding of the main blocks of Web3 technology, let’s move on to exploring this innovation further.
Key Concepts Driving the Web3 Ecosystem
Earlier, we briefly touched on these core elements. Now, let’s dive deeper into each, exploring their technical foundations and real-world impact — essentially expanding on what we covered before.
Blockchain and Smart Contracts
How Blockchain Ensures Trust and Security
Blockchains operate through decentralized ledgers that record every transaction in a transparent way. They leverage cryptographic designs for data integrity, which allows them to build trust among participants without centralized oversight.
The Role of Smart Contracts
Smart Contracts stand as self-executing agreements coded directly into a blockchain. They basically automate processes on the blockchain, whether payments or governance, to essentially remove any intermediaries and associated errors or delays.
Cryptocurrencies and Tokens
Utility and Governance Tokens
As we’ve already mentioned, cryptocurrency acts as the main medium of exchange across all decentralized ecosystems. Token exchange capabilities go beyond payments and grant access to services or voting rights in the governance structure of a network.
Role in Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
In DeFi platforms, cryptocurrencies and tokens enable borrowing, lending, and yield farming — replacing banks with transparent, programmatic alternatives accessible worldwide.
Decentralized Applications (DApps)
Features and Advantages
Rather than operating on centralized servers, DApps run on blockchain networks and offer censorship resistance, transparency, and user control over data. Their open-source nature is what fosters community-driven innovation.
Examples of Popular DApps
Prominent DApps include Uniswap (decentralized exchange), Aave (lending/borrowing), and Axie Infinity (blockchain gaming), each showcasing unique use cases within the Web3 ecosystem.
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs)
Governance and Decision-Making
DAOs shift organizational control from a central authority to token holders, who vote on proposals. This democratic structure is coded into smart contracts, ensuring transparent and fair governance.
Real-World Examples
Notable DAOs include MakerDAO (stablecoin governance), MolochDAO (funding public goods), and Aragon (DAO framework), illustrating practical applications across finance and community projects.
Why Web3 Is Important
1. Data Control
Web3 allows users to truly own their own data rather than centralized systems collecting, capturing, and monetizing it. By utilizing decentralized identity and blockchain, users will be able to better control what data they share and how it is processed – and in turn decrease reliance on big tech’s centrality and fragmentation, while promoting privacy, transparency, and control.
2. Financial Inclusion and DeFi
Decentralized finance (DeFi) removes many barriers to access and the traditional obstacles in the finance world. With DeFi, anyone with an internet connection will be able to save, borrow, invest, and trade without the need for a bank account or credit score. DeFi will offer the billions of underbanked and unbanked people around the globe an open and censorship resistant alternative to the old world of finance, without the reliance on trust by leverage standing on a public blockchain.
3. New Innovations and Business Models
Web3 allows for new forms of participation and ownership altogether. With the rise of tokens, NFTs, and DAOs, users will be able to own, govern, and benefit directly from the platforms they engage with, and creators will be able to monetize their creations directly to consumers with no middlemen. Communities will be able to pool funds together to develop and manage projects collaboratively. Overall, the direct transition will enable a wider range of user-focused innovation and inclusiveness.=
Web3: use cases
Here’s your brief web3 guide on key use cases within this innovative space.
DeFi
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is a fast-growing financial system within the Web3 sector that holds immense potential to improve traditional finance.
The appeal of DeFi propels its adoption and global market growth, which is projected to reach an astonishing $231 billion by 2030, expanding at a mind-blowing CAGR of 46%.
The DeFi ecosystem utilizes cryptocurrencies and encompasses a full suite of financial services:
- payments;
- loans;
- investments;
- trading;
- etc.
Unlike traditional finance, DeFi has a decentralized financial infrastructure – leverages blockchain and smart contracts – and thus can offer financial services in a decentralized way.
In this context, DeFi completely cuts out middlemen (banks, financial organizations) who facilitate financial operations and charge fees for their services.
This means that users can send money, lend, borrow, etc., using a dApp where financial services are managed in a peer-to-peer way and transparently recorded in decentralized financial databases maintained by all stakeholders.
The benefits?
- Much lower barriers to entry in finance;
- Agility and full control over personal assets and data;
- Global reach without any intermediaries;
- Unprecedented transparency;
- Reduced fees
NFT and asset tokenization
Hardly anyone hasn’t heard of NFTs yet. They’ve caused a real buzz in 2021, and the global market revenue is expected to reach $1,6 billion by the end of 2023.
Basically, NFTs represent verifiable one-of-a-kind digital goods that one can own and trade securely using blockchain technology.
Most likely, you’ve first heard of NFTs within the art and collectibles context.
They’ve created massive opportunities for artists and creators to showcase and monetize their works beyond the physical world and even earn royalties.
Some quick facts:
- Christie’s, a world-leading British auction house, has launched its own NFT marketplace after successful efforts with its NFT artworks, such as Beeple’s Everydays: The First 5,000 Days, sold for $69.3m in March 2021.
- A handful of luxury brands like Gucci and Burberry have tapped into the NFT space, launching their own digital collectibles. Several car brands like Porsche and Ferrari also joined the game and released exclusive NFTs featuring their iconic vehicles for their loyal fans.
- Many Hollywood celebrities have generated substantial value by selling their own NFTs, further driving public interest and adoption.
However, NFT use cases go far beyond art and collectibles.
Due to their digital nature, tamper-proof quality, and public interest, NFTs fostered many other innovative applications and monetization opportunities.
Here are a few prominent ones:
NFTs to incentivize purchases and customer engagement
Several companies, including Starbucks and Nike, experiment with NFTs to offer special discounts and exclusive access to product features, combine them with physical items, gamify brand interactions, and more. Just recently, airline giant Lufthansa launched its loyalty program Uptrip, which allows passengers to collect digital cards from their trips, complete collections, and redeem cool rewards, like business lounge vouchers.
NFTs to tokenize physical assets
Real-world items, like real estate and luxury goods, can be easily tokenized and divided into ownership fractions through NFTs. This empowers investors to easily diversify their portfolios with many fractional assets, which can be later traded and sold.
NTFs to facilitate financial services
Within the DeFi space, NFTs can serve as collateral for obtaining loans, facilitate borrowing and lending, and be used as an asset in betting markets.
Supply chain management
With blockchain and smart contracts, we’re witnessing a shift towards decentralized data control, heightened transparency, and streamlined complex processes.
And all of that is poised to transform industries that largely deal with logistics and supply chains.
Web3 seamlessly connects multiple stakeholders and allows them to engage and transact with a great degree of transparency and security without the involvement of intermediaries:
- track the flow of goods from the production stage to delivery;
- access and verify detailed product history;
- validate supplier data;
- record and securely store data and transactional details;
- automate lengthy processes like monitoring, transportation compliance, etc.
Proof of authenticity
Web3 technology stack allows for the creation of immutable digital certificates that aid in verifying the authenticity of physical items and digital assets, from art and collectibles to documents and luxury goods.
Lifewallet is a blockchain-powered solution for secure storage and validation of critical educational credentials (diplomas, certificates, etc.), pivotal for users’ career advancement and employment prospects. These records can be easily shared with prospective employers and educational institutions for verification of users’ expertise and qualifications.
Consider Kindgeek to seamlessly navigate the Web3 landscape
Kindgeek, a one-stop-shop fintech software development company, can help your business enter the Web3 world with clarity and take advantage of the latest advancements in the industry.
Whether you need a custom blockchain solution, smart contract development, or a decentralized finance (DeFi) platform, our team of experts has the skills and experience to deliver results.
Choosing us, you can also leverage our expert partner network to enhance your product while streamlining the development process and speeding up time to market.
Looking ahead
As technology advances, we may one day wake up in a whole new era called Web3. It’s a better version of the web, which has a large list of advantages. As Web3 is still immature, it has its drawbacks, but lots of investments and efforts are being made to reduce them.
For some new iteration of the web might seem alien or unrealistic. For some, it might seem superfluous, but let’s remind ourselves in the first place that the idea of the internet itself seemed very much the same.
Because who could have thought back then that technologies would reach so far and disrupt our lives so exponentially?
And coming back to our present-day reality, who can be sure of what the future holds? Maybe in 10 years’ time this ‘Web3’ thing will be the new norm.
Reality check: big tech companies are investing in blockchain, and many businesses all over the world are already in the process of figuring out the ways to approach Web3.
That’s why it is crucial for businesses not to stay aside, keep an eye on the latest trends in digital transformation, and prepare for the disruption unless they want to be left behind one day.
How do Web3 and blockchain fit together?
Recently updated on April 18, 2024
While Web3 is a future iteration of the internet, blockchain is one of its fundamental elements that make up its core.
How do Web3 and crypto relate?
Recently updated on April 18, 2024
While Web3 is a new, better version of the internet, crypto is a part of it, acting as a unit of value that you can earn, own, trade and buy almost everything with. It helps to fulfill the Web3 concepts, such as decentralization and equal access for all.
When will Web3 come into force?
Recently updated on April 18, 2024
No one knows for sure. It needs to become popular with the public to go mainstream. As of now it’s unlikely, as not so many people are well-versed in Web3 basics, but given appealing Web3 features and rapid market dynamics, this may change in years to come.
How do I authenticate on Web3 dApps?
Recently updated on April 18, 2024
The only thing you need to access Web3 applications is to have a crypto wallet.
What is the structure of Web3?
Recently updated on April 18, 2024
Web3 ecosystem consists of three main elements:
1) blockchain (decentralized apps aka dApps run there);
2) smart contracts (software that is deployed on blockchain to execute tasks autonomously)
3) digital assets — crypto tokens and NFTs (units of value used to arrange Web3 space)
What are the Web3 trends?
Recently updated on April 18, 2024
As the Web3 landscape is evolving, we can see maturation and greater adoption of DeFi, more focus on utility-based NFTs, a greater shift to sustainability and energy efficiency mechanisms, and increasing tokenization of physical assets.


