Recently updated on July 29, 2024
People seem ready to go all-in with a cashless style of life and forget about clunky wallets. To achieve this, society needs abundant fintech and convenient personal finance apps to make a cashless society a reality and ensure a healthy competitive market with reasonable prices, excellent customer experience, and the sector’s evolution. Do entrepreneurs who set out to create a mobile finance app know all the nuances of developing one? Quite likely, yes. However, better safe than sorry. We know plenty of nuances from experience and want to share this plenty with other enthusiasts.
In this article, you’ll read about popular personal finance management apps, the core functionality of the apps, the process of how to create a personal finance app and determine the costs, and the ways of monetisation.
Content:
1. Examples of Personal Finance Apps
2. What Do People Want to See in Personal Finance Apps?
3. How Creating a Financial App Can Help to Control Personal Finances
4. Functions of Personal Finance Apps
5. How to build a Personal Finance App
6. How Much Does It Cost to Develop a Personal Finance App?
7. Monetization of Personal Finance App
8. Conclusion
9. FAQ
Examples of Personal Finance Apps
Managing personal budgets, controlling spending, planning for the future, and efficiently dealing with finance-related operations is quite a task. Personal finance apps automate and digitise these processes, taking all the heavy accounting lifting off a user’s shoulders. Finance management apps come in different packages, with different “tastes and flavours” to suit different needs in various countries with unique mentalities and preferences. That’s a lot of synonyms, but you’ve got the gist of it. Also, consider that although most finance management apps have standard functionality, they have unique specialities. They aim at a certain audience or have unique features that separate them.
To better crack the essence of successful finance management apps, let’s take a look at a pair of the most popular specimens in the industry:
Mint
Mint is already an old-school app by the modern digital market standards. However, founded in 2008, Mint is still fresh and popular. It is a free personal finance app with 15 million users, which provides the following functionality:
– Connecting all user’s credit and debit accounts to a single interface
– Managing personal budgets, with expense planning per certain time period
– Geolocations tracker to monitor where spending was made
– Statistical visualisation of the relevant data: charts and graphs of spending and profits
– A variety of notifications and alerts to keep users informed, including dates when bills are due
– Extensive customisation
– Credit management
Overall, Mint is your Swiss knife of personal finance management systems. Mint is excellent, but the only downside is that the app is only for Canadians and US citizens. Also, with constant updates and proper maintenance, which helps to ensure the system’s relevance and competitiveness, Mint demonstrates the significance of proper software support. Mint runs on iOS, Android, and Windows Phone.
You Need a Budget
You Need a Budget (YNAB) is an app that helps people escape debt and “stop living paycheck to paycheck.” The key benefit of YNAB is that the app not only provides a user with the functionality to monitor and manage budgets but also with relevant advice and support on how to handle financial crises and avoid financial distress situations in the future. So, besides providing your ‘typical budgeting app’ features, You Need a Budget has a forum for financial advice and emotional support, prioritization guides, long-term goals advice, support on dealing with debts, saving guides, etc. It has versions for Windows, macOS, iOS, and Android.
What Do People Want to See in Personal Finance Apps?
In an age where financial literacy and management are crucial, personal finance apps have emerged as integral tools, offering a robust platform to navigate financial landscapes. As individuals seek greater control and understanding of their money matters, finance apps should offer various features tailored to meet these demands. From simplifying budgeting and expense tracking to providing insights for smarter decision-making, users seek specific attributes that transform these apps into indispensable companions on their financial journeys. Let`s take a look at some of the critical attributes users seek in a personal financial app:
User-Friendly Interface
An intuitive and easy-to-navigate interface is crucial. Users prefer simple apps that are easy to understand and operate, allowing them to access financial information effortlessly.
Comprehensive Financial Overview
Users want a holistic view of their finances in one place. This includes bank account integration, investment tracking, budgeting tools, expense categorisation, and financial data visualisation. Effective budgeting tools that allow setting budgets, categorising expenses, and tracking spending against these budgets are also highly sought after. The ability to generate reports or receive alerts for overspending is valuable.
Security and Privacy
Robust security measures to safeguard personal and financial information are non-negotiable. Users want encryption, secure login processes, and assurance that their data is protected.
Customization and Flexibility
Customizing features, categories, and reports according to individual preferences is appreciated. Additionally, syncing across devices for seamless access is also highly appreciated.
How Creating a Financial App Can Help to Control Personal Finances
The main purpose of a personal finance app is to help manage finances more effectively. These apps offer tools and features that assist in tracking income, expenses, budgeting, saving, investing, monitoring debts, and overall financial planning. The primary goal is to provide a comprehensive platform to gain better control over money, make informed financial decisions, and work towards financial goals, whether saving for a specific target, managing daily expenses, reducing debt, or planning retirement.
Besides its main purpose, personal financial apps may benefit users in many ways:
Financial Awareness and Education
These apps often educate users about various financial concepts, helping them understand budgeting, investing, saving strategies, and the impact of their financial decisions. They may provide tips, articles, and resources to enhance financial literacy.
Goal Setting and Planning
They enable users to set financial goals – whether short-term (like saving for a vacation) or long-term (like retirement planning). The apps assist in creating actionable plans to achieve these goals.
Financial Insights and Analysis
Through data visualisation and analytics, finance apps offer insights into spending habits, trends, and areas needing attention. This empowers users to make informed decisions.
Financial Empowerment
Ultimately, these apps aim to give users a sense of control and empowerment over their financial lives, fostering confidence and peace of mind regarding their monetary decisions.
Functions of Personal Finance App
To make a personal finance app, you should know its primary and additional features. The former makes an app relevant, and the latter makes it interesting. Thus, the functions of money management personal finance apps are:
Essential functions of a finance app:
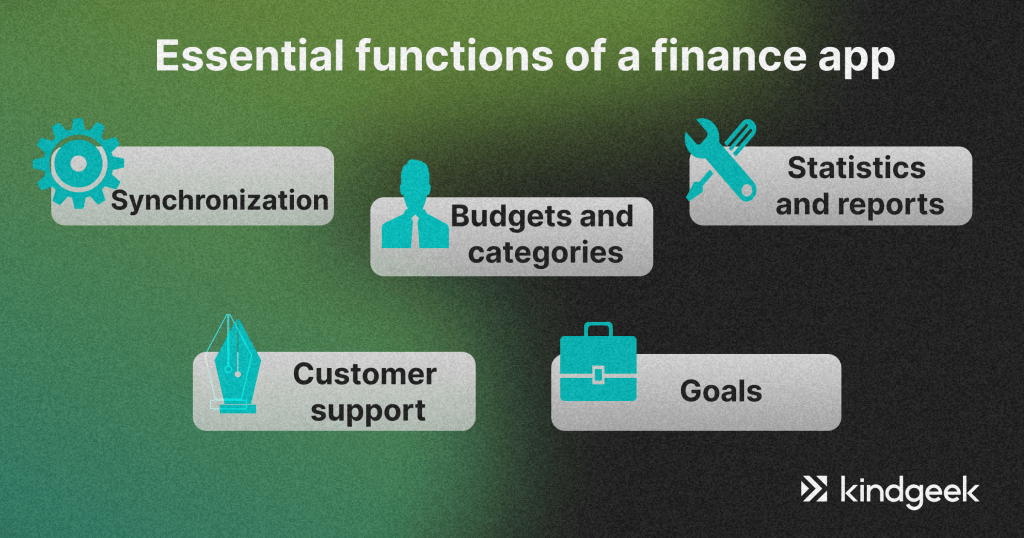
Synchronization with a user’s bank and credit accounts to keep track of budgets, which also may include investments and loans. While synchronising, an app should download data on previous transactions that occurred in recent months to provide some initial statistics.
Budgets and categories. A user should be able to create categories for expenses and set budgets accordingly. An app should assign categories to transactions automatically based on the provided data. The more innovative your personal finance app is, the better. Let the app automatically set the limits of the budgets based on transaction statistics and provide additional advice.
Goals. Setting short or long-term financial goals tied to certain budgets is a must for a personal finance app. The software should also help to reach set goals using notifications and alarms.
Statistics and reports. Sometimes, beautifully organised data showcased with the help of accurate and insightful charts and graphs and nicely-tuned reports are the best way of motivating people to stay on track with their financial goals. All in all, aim for the stars and try to develop the best app for creating personal finance reports.
Customer support. As always, there is no reliable fintech app without proficient and stress-resilient customer support, which is always there to help newcomers and other users figure out stuff and deal with users’ frustrations.
Pleasant add-ons of a finance app:

Monitoring of investments. Keeping people informed on the condition of their investments, comparing market indices, etc
Guides and personalised advice. Guides about money management and ‘lifehack’ that help to save more are a nice feature, which also sends users the message “We care.”
Forums and support. Take YNAB; its forums with support and advice from other people who help each other deal with financial problems or improve financial habits are major selling points.
Talking about features and functions…
“Ahem… Hello, do you have a spare minute to talk about security of personal finance apps?”
There’s no avoiding talking about security when the deal gets to fintech. We’ve already talked about it, we are talking about it now, and we’ll talk about it again. Security is where overt repetition is justified. Many money and sensitive information are lost due to crafty cyber attacks and mishaps. And while people somewhat tolerate the potential vulnerability of personal data, money security is not what they’re willing to risk.
Users want secure financial apps, and you want your app to be as secure as possible. Make security the heart of the money management app development, and find a team that knows how to make the software bulletproof. The security of an app starts with basics, such as an approach to writing code, lasts throughout each development stage, and ends with third-party service selection and integration, so it’s better to be cautious of each step along the way. You can read more about the basics here.
How to Build a Personal Finance App?
Developing complex software is an epic tale in several chapters because of the initial market research, thorough planning, development, and testing required to build a robust product. Personal finance app development is not an exception. Be it a personal management app for iPad, a personal expense tracker Android app, or a personal expense tracker app for iPhone, the plan for the development is the same. In broad strokes, if you are looking for how to create a financial app from scratch, the plan is the following:
Idea & Research
During this stage, business analysts, software developers, and QA specialists shape the blueprint of the future system based on functional and non-functional requirements, regulatory environment compliances, market research, and competitor analysis.
Design
Creation of personal finance app visuals by UI/UX designers considering the results of the previous research, requirements of platforms, stakeholders, and fundamentals of intuitive user experience.
Here, at KindGeek, we combine the first and second stages into the Discovery Phase, a neat condensed package of all necessities required for further development, funding, and cost estimates.
Development
The development is a complex process involving separate iterative stages, called sprints, divided into smaller phases, such as planning development, testing (QA phase), and review. The iterative nature of the development allows for continuous building and polishing of the product. At the same time, tight communication with the stakeholders and owners is present to consider feedback.
Support & Maintenance
After the product is developed, it’s time to support and maintain it, update its functionality, adapt it to new circumstances, and deal with bugs.
Of course, the app development plan can vary depending on the state of the idea, research required, state of investments, etc. However, if we are talking about creating a personal finance app from scratch till completion, that’s the route we adhere to create lasting and relevant tech. However, remember that software development is flexible and adjustable, and finding a proper approach to any case is possible.
How Much Does it Cost to Develop a Personal Finance App?
Measuring the price of software development is … tricky. It’s not like building a table, where we know the price of materials and, with enough experience, can estimate how much time it will take to complete it ‘by eye.’ With software, the situation is more complicated and requires a thorough analysis. to consider requirements, regulatory environment, tech stack, third-party services, number of features to develop, time for developing each feature, etc.
Estimating costs takes some time and varies in accuracy depending on the thoroughness of the analysis. Perhaps the surest way of determining the price is the aforementioned Discovery Phase, which, depending on a chosen package, will provide accurate cost estimates and:
– product concept from Product Manager
– prototypes from Business Analyst
– visual concept from UI/UX Designer
– architecture concept from System Architect
Monetization of Personal Finance App
It’s all sweet and neat, but how do personal finance apps make money? Of course, you can charge money for an app. For instance, Quicken is for sale and appears quite a successful contender. However, remember that people are not used to paying for apps. If you decide to charge for the software, the marketing for the product should be immaculate and articulate why the app is worth the price in a surprisingly engaging and convincing way.
Currently, free or almost free options are the trend. Therefore, the following ways of personal finance app monetisation are the most prevalent:
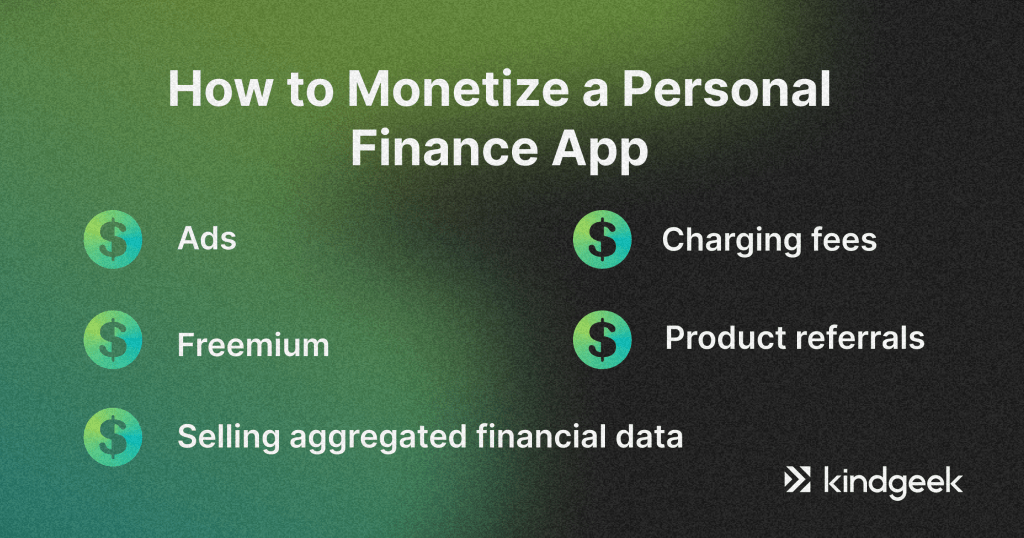
Ads. They can be frustrating and distracting, but they do the job. Also, users can pay to get rid of them.
Freemium. The free app, but extra features for sale. For example, essential features, such as budgeting and categorisation, can be free, while investment management or personalised guides — are for sale. However, deciding which functionality to monetise should involve a lot of market research.
Selling aggregated financial data and including product referrals is another way of monetisation. For instance, Mint practices it.
Charging fees for certain services, such as investment portfolio management.
Finally, you can be creative and ‘invent’ new ways of monetisation that will be unique and feasible for your product.
Conclusion
Budgeting, keeping track of expenses, and managing banking accounts can be daunting. You can make it easier for people by developing a relevant app. The market is ripe for such endeavours; finding the right opportunity and targeting the right audience is essential.
If you are set to create a mobile finance management app, a personal expense tracker app, budgeting software, or any other fintech tech, you’ll have to endure quite a long journey. However, we can help. With experience developing fintech and mobile apps of various complexities, we know how to make the journey a breeze.
What is the process of a money management app development?
Creating a money management app involves defining key objectives, conducting market research to understand user needs, designing intuitive interfaces, ensuring robust security measures, selecting the appropriate development platform, testing thoroughly, launching, and continuously improving based on user feedback.
What should be considered in personal finance mobile app development?
Remember that you are creating an app for a user, so considering their preferences is necessary. They seek a user-friendly interface, comprehensive financial overview, security and privacy customisation, and flexibility.
What features should be included while creating a finance app?
To make a personal finance app, you should know its primary and additional features. Primary: synchronisation with a user’s bank and credit accounts, budgets and categories, goals, statistics and reports, and customer support. Additional: monitoring of investments, guides, personalised advice, forums, and support.


