Recently updated on April 18, 2025
Core banking software is the backbone of modern banking operations, providing a comprehensive suite of solutions to manage critical functions such as deposit accounts, loans, and customer interactions. At its core, this software serves as a centralized data repository, enabling banks to maintain accurate and up-to-date records of customer accounts, transactions, and related information.
In an era of digital transformation and increasing customer demands, understanding core banking systems is crucial for financial institutions looking to stay competitive. This article explains how does core banking software work, its key components, and how emerging technologies are reshaping it to meet modern banking needs. Whether you’re modernizing legacy systems or evaluating new solutions, you’ll gain practical insights into the technology that powers today’s banking operations.
What Is Core Banking?
According to Gartner Glossary, a core banking system is a back-end system that processes daily banking transactions and posts updates to accounts and other financial records. Core banking systems typically include deposit, loan, and credit processing capabilities, with interfaces to general ledger systems and reporting tools.
The term CORE stands for Centralized Online Real-time Environment, meaning that customers, regardless of location, can experience the bank as a single unit. It allows the existing and probable customers to have more independence in terms of using their accounts and conducting transactions from any location in the world.
With technological evolutions, transactions are now safer, faster, and less cumbersome. The fact that these transactions can be done remotely, no matter the user’s location, has made core banking systems a significant aspect of banking these days.
As was already mentioned, core banking is a back-end computer system used to support an array of the most common day-to-day banking transactions. These transactions include:
- Opening and managing accounts.
- Managing deposits and savings.
- Managing payments and cards.
- Calculating interest.
- Conducting customer relationship management (CRM) activities.
- Setting criteria, such as minimum balance, interest rates, or the number of permitted withdrawals.
- Lending, generating, and managing loans.
- Managing the recording of all banking transactions, regulatory reporting, and data processing.
What Are The Types Of Core Banking Systems?
On-premise legacy solution
These traditional systems run on local infrastructure, offering banks direct control and customization capabilities. While robust and time-tested, legacy systems often run on older programming languages, creating a significant technical debt. Their monolithic core banking system architecture makes integrations complex and time-consuming, requiring specialized knowledge that’s becoming increasingly scarce in the job market.
Many banks continue operating on core systems developed decades ago, not necessarily due to preference, but because these systems are deeply embedded in their operations and handle millions of daily transactions reliably. However, their rigid architecture and outdated technology stack significantly limit the bank’s ability to implement modern features, integrate with fintech solutions, or respond quickly to market changes.
To address these limitations, many financial institutions are investing in modernizing their core banking systems, opting for cloud-native solutions and digital platforms that offer greater flexibility, scalability, security, and customer-centric features.
Cloud-based solution
Modern cloud-based core banking operates on a fundamentally different principle: it treats banking capabilities as composable services rather than a monolithic system. Whether deployed as Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) or through Cloud-as-a-Service (CaaS) models, these solutions eliminate the need for extensive hardware infrastructure while offering consumption-based pricing.
The cloud approach enables banks to leverage microservices architecture, API-first design, and continuous deployment capabilities. This translates into faster innovation cycles, easier third-party integrations, and the ability to launch new products in days rather than months. While the transition costs are substantial and data security concerns must be carefully addressed, the long-term benefits in terms of competitiveness, customer satisfaction, and operational efficiency can outweigh the drawbacks.
Benefits Of Using Cloud-Based Core Banking
The adoption of cloud-based core banking delivers transformative benefits across the entire banking ecosystem. For financial institutions, it revolutionizes operational capabilities and business agility, while customers enjoy enhanced services and a more responsive banking experience. Let’s examine how cloud-based core banking creates value for both banks and their customers, driving the future of financial services.
| for customers | for the business |
|---|---|
| 24/7 Accessibility Cloud-based systems allow customers to access their accounts and conduct banking transactions 24/7 from anywhere with an Internet connection. Clients can also contact customer support for assistance at any time. | Cost Efficiency Cloud-based core banking eliminates the need for businesses to invest in and maintain expensive on-premises hardware and infrastructure. They can pay for cloud services on a subscription or pay-as-you-go basis, reducing capital expenditures. |
| Multi-Channel Banking Customers can perform banking activities through various channels, including web browsers, mobile apps, and smart devices. This flexibility enables customers to choose the most convenient method for their needs. | Scalability Cloud solutions are highly scalable, allowing businesses to adjust their computing resources and capacity as needed. This scalability is particularly beneficial for banks and financial institutions that need to accommodate growing customer bases and increased transaction volumes. |
| Faster Transaction Processing Cloud-based systems often offer faster transaction processing times, reducing the time it takes for funds to be transferred and making services more efficient. | Faster Implementation Cloud-based core banking systems can be implemented more quickly compared to traditional on-premises solutions. This accelerated deployment allows businesses to bring new banking services and products to market faster. |
| Real-Time Updates Customers can receive real-time updates on their account balances and transaction history, providing accurate and up-to-date financial information. | Accessibility and Mobility Cloud-based systems can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection. This accessibility enables remote work, which has become increasingly important in today’s business environment. |
| Enhanced Security Core banking systems use advanced encryption modules to protect the infrastructure from hackers and malware. Customers can benefit from the advanced security features provided by cloud-based core banking systems. | Data Security and Compliance Cloud providers typically invest heavily in security measures and compliance certifications. Businesses can benefit from the advanced security features and expertise provided by cloud vendors, helping them meet regulatory requirements and protect customer data. |
| Innovation Cloud-based core banking systems can quickly integrate new features and services, enabling banks to offer innovative products and functionalities to customers. This includes features like budgeting tools, financial planning, and AI-driven insights. | Innovation and Agility Cloud-based systems can quickly adopt new technologies and innovations. This enables businesses to stay competitive by offering innovative financial products, services, and features to customers. |
| Customization Banks can customize their cloud-based core banking systems to meet the specific needs of different customer segments. This can lead to more personalized and tailored banking experiences. | Global Access Cloud-based systems make it easier for customers to access banking services when travelling internationally, reducing the need for currency exchange and providing a consistent banking experience across borders. |
| Enhanced Security Core banking systems use advanced encryption modules to protect the infrastructure from hackers and malware. Customers can benefit from the advanced security features provided by cloud-based core banking systems. |
Do Core Banking Systems Have Limitations?
There are many advantages of core banking solutions. However, they also come with their own set of limitations and challenges, including:
1. Downtime and Availability
While cloud providers generally offer high availability, downtime can still occur due to maintenance or unexpected outages. Banks need to have contingency plans in place to ensure uninterrupted banking operations and customer service during such events.
2. Integration Challenges
Integrating cloud-based core banking systems with legacy on-premises systems can be challenging. Ensuring seamless data flow and interoperability may require substantial effort and investment.
3. Data Migration
Migrating existing data from legacy systems to the cloud can be a complex and time-consuming process. Data quality and integrity must be maintained during migration.
4. Cost Management
While cloud solutions can be cost-effective in the long run, costs can spiral if not managed effectively. Banks need to monitor usage and optimize their cloud infrastructure to avoid unexpected expenses.
5. Challenging Software Implementation
Considering the impressive scale of banking system logic, the complexity of processing transactions, required investments, and tight regulations, when a deal gets to core banking software implementation, different challenges arise.
Architectural Framework of Core Banking Solutions
At the heart of every core banking system lies a robust architectural framework that defines how core banking system works, facilitates efficient operations and seamless integration with various banking channels.
The core banking application architecture part is the central component, managing critical functions such as account opening, transaction processing, loan management, and customer relationship management. Underpinning this application is a powerful database management system, which is responsible for storing and managing the vast volumes of customer data, transaction records, and other banking information that form the institution’s lifeblood.
Enabling customer access are channels and delivery components facilitating interactions through branch networks, ATMs, internet banking, and mobile apps. An integration layer connects the core system with other platforms like treasury management, risk management, and regulatory reporting, ensuring seamless data exchange.
Robust security and authentication components, including user authentication, access controls, and encryption protocols, safeguard data integrity and privacy. Reporting and analytics tools provide valuable insights into customer behaviour, transaction patterns, and operational performance, driving data-driven decision-making.
Middleware and message queuing systems facilitate efficient communication and data transfer between architectural components, enabling real-time processing. Business process management components streamline and automate critical processes like loan origination, account opening, and customer onboarding, ensuring consistent execution and enhanced productivity. This modular and integrated core banking software architecture ensures scalability, flexibility, and the ability to adapt to changing business requirements and technological advancements, positioning banks for long-term success in an ever-evolving landscape.
Functional Capabilities of Core Banking Solutions
Core banking systems are expected to process countless transactions daily while managing vast customer data and financial records. Though solutions may vary slightly across vendors, several key features and functionalities that define core banking system works are essential for delivering maximum value.
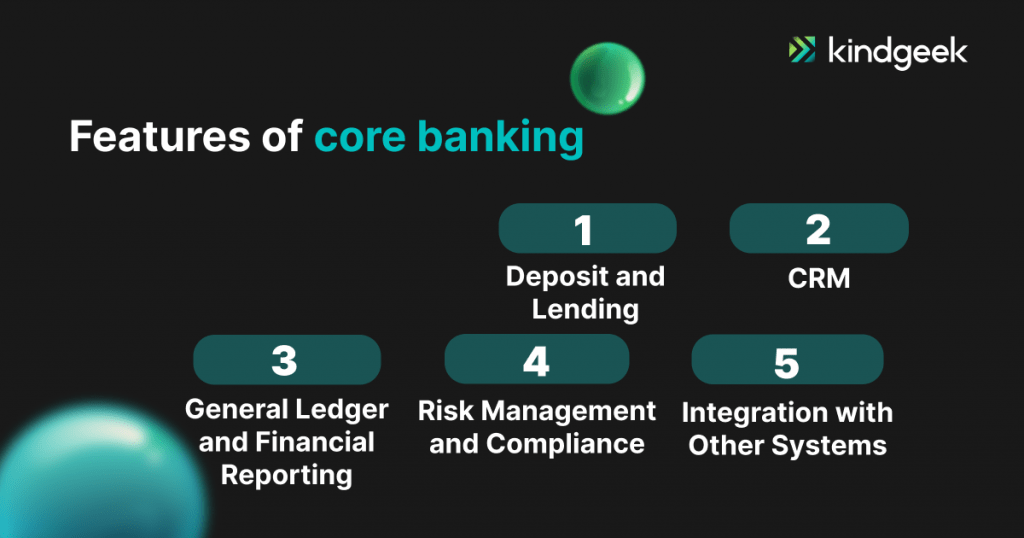
Let`s start with a couple of main ones:
Deposit and Lending Operations
Core banking software is instrumental in managing the lifeblood of any banking institution: deposit and lending operations. From account opening and management for various product types, such as savings and checking accounts, to loan origination and servicing for mortgages and personal loans, these functionalities streamline processes and provide a centralised platform for handling transactions, including deposits, withdrawals, and transfers.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
In today’s customer-centric banking landscape, core banking software plays a pivotal role in cultivating strong relationships with clients. Comprehensive CRM functionalities enable banks to maintain detailed customer data and profiles, effectively manage inquiries and service requests, and identify cross-selling and upselling opportunities for products and services tailored to individual needs.
General Ledger and Financial Reporting
Accurate financial reporting is crucial for informed decision-making and regulatory compliance. Core banking software solutions encompass robust general ledger management capabilities, enabling banks to maintain a comprehensive record of their financial transactions. Furthermore, these systems generate critical financial statements and regulatory reports, ensuring transparency and adherence to industry standards.
These functionalities work even better in cooperation with other additional features to provide a comprehensive solution for managing various aspects of banking operations, ensuring efficient customer service, regulatory compliance, and overall business growth.
Let`s overline them as well:
Risk Management and Compliance
As the regulatory landscape evolves, core banking software has emerged as an indispensable ally in mitigating risks and ensuring compliance. Advanced functionalities for anti-money laundering (AML) and fraud detection, coupled with robust mechanisms for adhering to regulations such as Basel III and GDPR, empower banks to operate with confidence and integrity.
Integration with Other Systems
In today’s interconnected banking ecosystem, core banking software must seamlessly integrate with a spectrum of other systems and services. Whether interfacing with payment gateways, treasury management systems, general ledger accounting software or enabling omnichannel banking experiences through integration with third-party applications, these functionalities ensure a cohesive and efficient operational environment.
Innovations Shaping the Future of Core Banking Software
As the financial services landscape continues to evolve at a rapid pace, driven by technological advancements and changing customer expectations, core banking software solutions are undergoing a transformative shift. Traditional systems that once served as the bedrock of banking operations are now being reimagined, embracing cutting-edge innovations to meet the demands of the modern era.
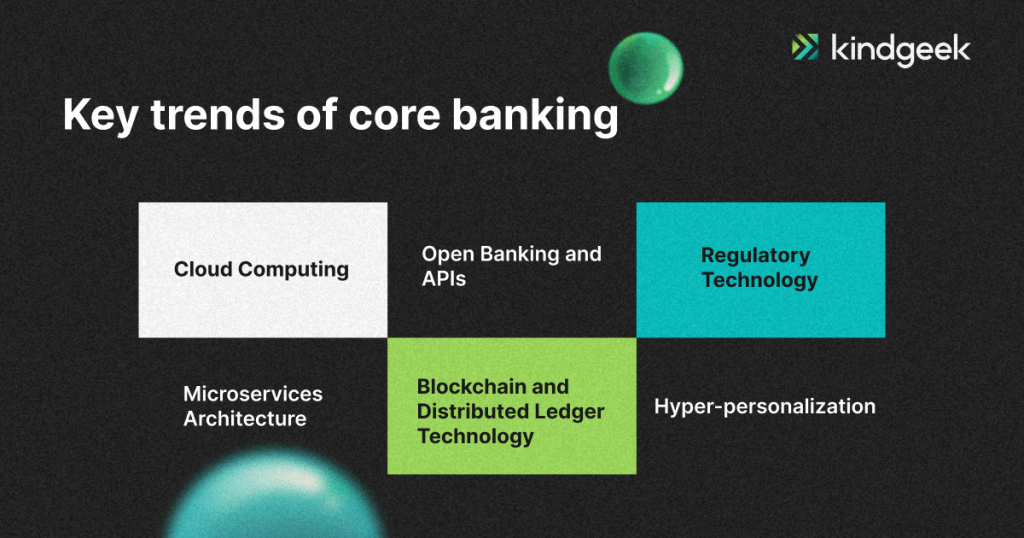
There are many trends shaping these changes. Some of them are in their final stages of becoming a global standard, while others are just starting to gain popularity. Let`s start with already well-known practices:
Cloud Computing
Many banks are moving their core banking systems to the cloud, leveraging cloud-based solutions. This shift offers several benefits, including scalability, cost-efficiency (pay-as-you-go pricing models), easier maintenance and updates, increased security, and business continuity/disaster recovery capabilities. However, data privacy, regulatory compliance, and potential vendor lock-in risks still need to be addressed.
Open Banking and APIs
Open banking involves banks providing secure, regulated access to customer data and services through APIs (Application Programming Interfaces). This enables third-party developers to build innovative applications and services on top of the bank’s data and infrastructure. It promotes competition, innovation, and improved customer experiences.
APIs can expose everything from account information and transactions to lending and payment services. Major regulatory frameworks like PSD2 in Europe are driving open banking adoption.
RegTech (Regulatory Technology)
As banking regulations continually evolve and become more complex, RegTech solutions help banks ensure compliance through automation and advanced technologies. This includes tools for risk management, anti-money laundering (AML), know-your-customer (KYC) processes, transaction monitoring, reporting, and more. RegTech helps banks streamline compliance efforts, reduce costs, and mitigate risks associated with non-compliance.
As we look towards the future, even more disruptive trends are on the horizon. While current trends are already reshaping the industry, these future directions are set to push the boundaries of innovation, enabling financial institutions to stay ahead of the curve and meet the ever-evolving demands of the modern banking landscape.
So, what trends are we talking about?
Microservices Architecture
Traditional monolithic core banking systems are being replaced by more modular, microservices-based architectures. Each microservice is a small, independent component that handles a specific business capability (e.g., account management, loan processing). This enables greater agility, as individual microservices can be updated or replaced without impacting the entire system. It also improves scalability, as different components can scale independently based on demand.
Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
While still in exploratory stages, blockchain and DLTs offer potential benefits for banking, including secure and transparent transactions, automated smart contracts, reduced settlement times, and disintermediation of certain processes. Applications range from cross-border payments and trade finance to digital identity management and regulatory reporting. However, challenges around scalability, interoperability, and regulatory acceptance need to be addressed.
Hyper-personalization
This trend leverages data analytics, AI, and machine learning to deliver highly individualised banking products, services, and experiences. By harnessing customer data insights, detailed profiles are created to predict needs and provide contextually relevant recommendations and tailored user experiences across touchpoints. As customer expectations grow, this real-time adaptability fosters deeper relationships, increased loyalty, and optimised lifetime value. However, robust data management, privacy protection, and ethical AI practices are crucial for the responsible implementation of this high-impact trend.
Surely, the list of future trends will keep expanding, and we can`t wait to see what they bring to the table.
Conclusion
As we navigate through rapid technological advancement and changing customer expectations, core banking software continues to evolve from a back-office necessity into a strategic enabler of financial innovation. The rise of embedded finance, open banking, and AI-driven services has made modern core banking systems more crucial than ever, serving as the foundation for new business models and revenue streams.
The future of banking lies in intelligent, adaptable core systems that can seamlessly integrate with fintech ecosystems, support real-time operations, and deliver personalized experiences at scale. Banks that leverage advanced analytics, machine learning, and cloud capabilities within their core systems will be better positioned to meet emerging customer needs, from embedded banking services to sustainable finance offerings.
As we look forward to this exciting future, it is very important for financial institutions to embrace a mindset of continuous innovation, fostering an environment that encourages experimentation and agility. It is only through such a forward-thinking approach that the true potential of core banking software can be realised, ushering in a new era of financial services that redefines the very notion of what it means to bank in the digital age.
And if you are looking for a way to speed up your core banking journey, you can also consider a white-label solution. In partnership with SDK Finance, Kindgeek offers a customer-centric, cloud-based SaaS fintech solution to serve as a foundation for digital finance products. The customizable white-label core allows you to build on top of it and create a unique customer experience. No need to start from scratch – go to market quickly and cost-effectively.
What is the meaning of core banking solution?
Recently updated on March 7, 2025
Core banking definition – it is a centralized system that processes banking transactions across multiple channels. It works by maintaining a unified database for customer accounts, automating transactions, and enabling real-time processing of deposits, withdrawals, loans, and other banking services across the entire network.
What are the main types of core banking software platforms?
Recently updated on March 7, 2025
On-premises systems: Traditional platforms maintained on the bank’s own hardware infrastructure, offering control but requiring significant IT resources.
Cloud-based systems: Modern solutions hosted on remote servers, providing scalability, reduced maintenance costs, and easier updates.
What are the main benefits of core banking solution?
Recently updated on March 7, 2025
Among a big list of benefits: centralised data management and processing; automated core banking operations; enhanced customer experience across channels; better risk management and regulatory compliance; scalability and flexibility to support growth.


