It is not a secret that it is almost impossible to imagine the world of fintech without open banking. This concept, which revolves around the idea of providing third-party financial service providers access to a consumer’s financial information through APIs, opens up traditional banking systems to external parties, fostering collaboration, innovation, and competition within the financial industry. But what is open finance, and does it have something to do with open banking? In this piece, we will aim to provide you with those answers and more.
We are also happy to share that this article was composed in collaboration with our partner, SaltEdge. Our partnership started in July 2023 and quickly boosted our ability to create impactful solutions, enabling businesses and individuals to thrive in fintech.
Kindgeek’s expertise in delivering custom fintech software solutions to businesses worldwide, combined with SaltEdge’s comprehensive range of open banking technologies and solutions, provides unparalleled value to our clients and promotes the growth and transformation of the fintech sector.
This partnership brings together Kindgeek’s proven track record in fintech software development with Salt Edge’s extensive experience in open banking and financial data aggregation. It also allows us to provide deep and intricate insights for this article.
Just keep reading!
What is open finance and is it different from open banking?
If open baking is all about sharing customer banking data through secure APIs, then what is open finance about? The definition is very similar: open finance has the same principles of data sharing, but if open banking focuses on traditional banking data and services, open finance extends to the entire financial services ecosystem, including investments, insurance, pensions, etc.
Therefore, consumers are gaining greater control over their financial information and accessing a wider range of financial services and products from various providers. How exactly does it work?
Data sharing infrastructure
The foundation is built on APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) that allow different financial institutions and services to securely communicate and share data. These APIs create standardized ways for systems to exchange information while maintaining security and privacy.
Authorization
The authorization process requires the customer to give explicit consent for their data to be shared. This permission is usually granular, meaning they can choose what data to share and for how long. Authorization is typically done through strong authentication methods like two-factor authentication.
Data flow
The process begins when a customer uses an open finance service. Financial data is collected from various sources, such as banks, investment accounts, and insurance providers. This data is then standardized and aggregated before being made available to authorized service providers that were approved.
The service layer enables financial service providers to use this data in multiple ways. They can create comprehensive financial dashboards, offer personalized financial advice, develop tailored financial products, automate financial processes, and provide risk assessments.
Security measures
The entire system is protected through encryption of data in transit and at rest, regular security audits, compliance with financial regulations, access controls and monitoring, and data minimization principles.
Open finance enables broader access to financial data and fosters innovation across diverse services like banking, investments, and insurance. However, as with any transformative technology, it comes with both significant benefits and potential challenges that must be carefully weighed. Let`s take a look at them together.
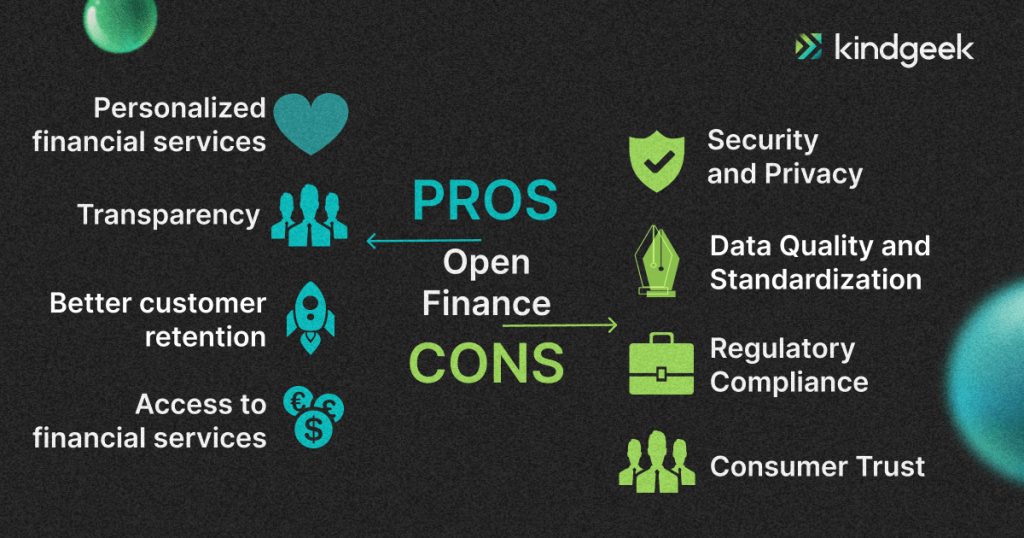
How can open finance benefit your business? (provided by SaltEdge)
In October 2024, the UK reported an impressive 1,747.3 million successful API calls and nearly 12 million active open banking users. Building on this quick and continuous growth, open finance is expanding the principles of open banking to unlock even broader applications and advantages for data, benefiting both consumers and businesses.
Personalised financial services
Open finance includes financial data about insurance, investments, loans, pensions, mortgages, and more. With access to such information, authorised entities can create personalised financial products and services based on customers’ preferences and habits. Businesses can further enrich these with tailored advice, like savings and investment strategies, or develop budgeting tools to help clients manage their finances more effectively.
Brazil exemplifies successful open finance adoption. By November 2024, the country had recorded over 37.7 million unique consents since its 2021 implementation. This allows clients to share data securely and receive personalised offers tailored to their specific needs.
“On the other side, businesses that leverage customer insights and shared data to develop new products and services promote innovation and boost the competitive advantage in the market, positioning themselves as a top-tier provider among traditional financial services.” – Alina Beleuta, Chief Growth Officer.
More transparency equals a better customer experience and retention
By consenting to share their financial information, clients gain control over their data and enjoy a comprehensive view of their finances. This transparency allows consumers to easily compare financial products, such as loans or insurance policies, from different providers and make well-informed decisions.
“In Brazil, customers are already benefiting from open finance by receiving personalised proposals based on their financial history without having to establish fresh relationships with new institutions. For example, a customer comparing loan offers might receive a 7.5% rate from their bank but discover a 4.5% rate elsewhere after sharing their financial data. This approach fosters competitiveness and empowers customers to make informed financial decisions while allowing them the flexibility to choose from multiple providers” adds Alina.
Access to financial services for the underbanked
With alternative data sources, open finance bridges gaps for the underserved population. People with limited or no credit histories can qualify for financial services like microloans or budgeting apps.
“By analysing non-traditional data sources, such as utility payments, rent records, or mobile phone bill history, businesses can assess creditworthiness more effectively. This enables them to develop individualised approaches, offer personalised products, and tap into new markets for new financial products,” shares Alina.
What challenges does open finance bring?
The rapid evolution of open finance brings transformative opportunities to the financial sector, promising greater transparency, innovation, and accessibility. However, as this technological advance unfolds, it also presents significant challenges that need careful consideration. Understanding these challenges is crucial for anyone looking to participate in or benefit from the open finance ecosystem. Let`s take a closer look:
Security and Privacy
As usual, the storage and sharing of financial data will cause the primary concern, which is security. With financial data being shared across multiple platforms and providers, the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access increases. To benefit from open finance, you must invest heavily in cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive financial information from sophisticated cyber threats.
Data quality and Standardization
Here is another major challenge. Different financial institutions often use varying data formats and standards, making it difficult to ensure consistent, accurate data integration. This inconsistency can lead to errors in financial analysis and decision-making.
Regulatory compliance
As open finance operates across different jurisdictions, organizations must navigate varying regulatory requirements and data protection laws. Staying compliant while operating globally can be particularly challenging due to different countries having different approaches to financial data sharing.
Consumer trust
You may face the challenge of many consumers remaining sceptical about sharing their financial data, often due to security concerns or lack of understanding about how their data will be used. Building trust while educating users about the benefits and safeguards of open finance is a must.
While these challenges may seem daunting, they shouldn’t overshadow the transformative potential of open finance. As technology advances and regulatory frameworks mature, many of these obstacles are being actively addressed through industry collaboration, innovative solutions, and evolving best practices.
Conclusions
Open finance represents a transformative shift in the financial ecosystem, offering unparalleled opportunities for consumers and businesses alike. By enabling a more comprehensive view of financial data, open finance empowers individuals to make informed decisions, access personalized products, and achieve financial wellness. At the same time, it fosters innovation, competition, and collaboration in the industry, unlocking new avenues for growth and customer engagement.
While challenges such as data privacy, regulatory complexities, and consumer trust remain, these should not stop you. With continued advancements in technology, collaboration among stakeholders, and the development of robust frameworks, open finance is poised to improve the financial landscape. The future of open finance is challenging but interesting, promising a world where financial services are more transparent, inclusive, and customer-focused.


